NIST AI RMF: Practical Steps for R&D Compliance by Mid-2025

The NIST AI Risk Management Framework provides a structured approach for organizations to identify, assess, and manage risks associated with artificial intelligence, crucial for R&D compliance by mid-2025.
Are you prepared for the sweeping changes coming with the new NIST AI Risk Management Framework: Practical Steps for R&D Compliance by mid-2025? This framework is set to redefine how AI is developed and deployed, especially within research and development, demanding a proactive approach to risk management and ethical considerations.
Understanding the NIST AI RMF Landscape
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) introduced the AI Risk Management Framework (RMF) to address the growing complexities and potential societal impacts of artificial intelligence. It serves as a voluntary framework designed to help organizations manage the risks of AI systems, promoting trustworthy AI development and deployment. For R&D teams, understanding this landscape is not just about compliance, but about building more robust, ethical, and reliable AI from the ground up.
The framework emphasizes a holistic approach, moving beyond mere technical specifications to include considerations of societal impact, fairness, transparency, and accountability. This means R&D departments must integrate risk management into every stage of the AI lifecycle, from conception to deployment and monitoring. Failing to do so could result in significant reputational damage, legal liabilities, and erosion of public trust.
Key Principles of the Framework
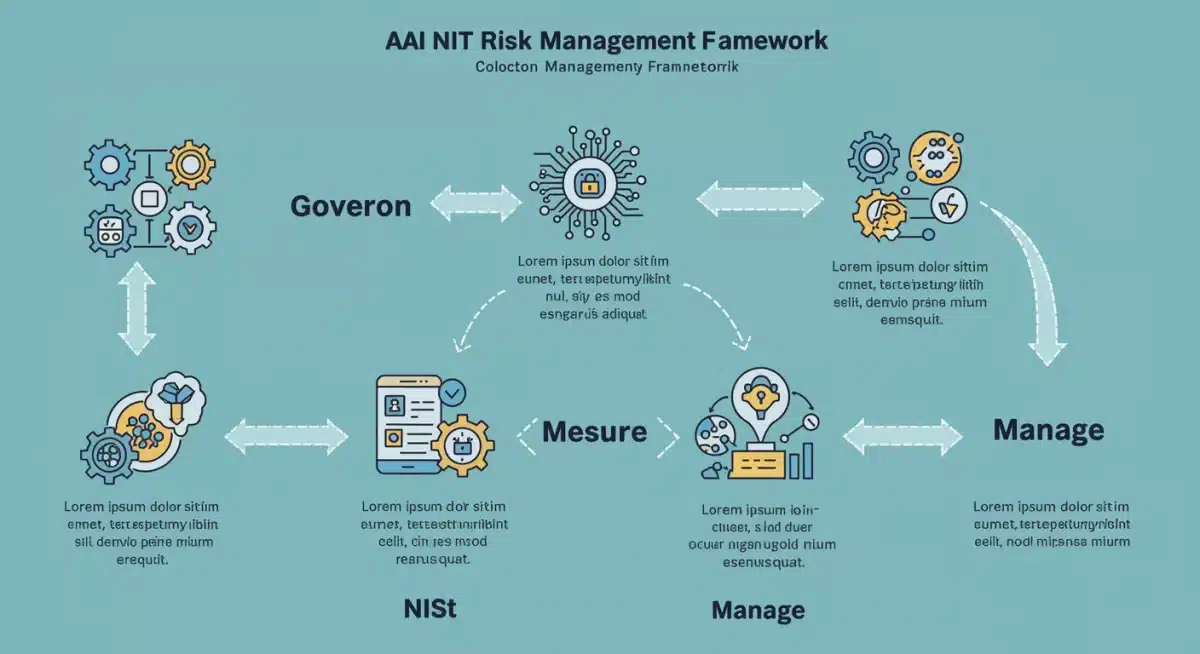
- Govern: Establishing a culture of risk management for AI, with clear policies and procedures.
- Map: Identifying and understanding the context, capabilities, and potential risks of AI systems.
- Measure: Quantifying, evaluating, and tracking AI risks and their impacts.
- Manage: Allocating resources and taking actions to address AI risks.
These core functions are interconnected and iterative, forming a continuous cycle of improvement and adaptation. For R&D, this translates into embedding these principles into project planning, design, development, and testing phases. It’s about shifting from a reactive stance to a proactive one, where potential risks are anticipated and mitigated before they become problems. The framework encourages collaboration across departments, ensuring that legal, ethical, and technical perspectives are all considered.
In conclusion, the NIST AI RMF is more than just a regulatory hurdle; it’s a blueprint for responsible AI innovation. R&D teams that embrace its principles will not only ensure compliance but also enhance the quality and trustworthiness of their AI systems, fostering greater acceptance and impact.
Integrating AI RMF into Your R&D Lifecycle
Integrating the NIST AI RMF into the R&D lifecycle requires a systematic and deliberate approach. It’s not an afterthought but a foundational element that should guide every stage of AI development. From initial concept generation to final deployment, risk considerations must be front and center. This integration ensures that ethical dilemmas and potential biases are addressed early, preventing costly rework and reputational harm down the line.
The process begins with a thorough assessment of existing R&D practices and identifying gaps where AI RMF principles can be embedded. This might involve updating standard operating procedures, introducing new checkpoints, or developing specialized training for R&D personnel. The goal is to create a seamless workflow where risk management is an inherent part of innovation, not an external imposition.
Designing for Trustworthy AI
- Fairness: Ensuring AI systems do not perpetuate or amplify harmful biases.
- Transparency: Making AI systems understandable and their decisions explainable.
- Accountability: Establishing clear lines of responsibility for AI system outcomes.
- Privacy: Protecting sensitive data used by AI systems.
These design principles are critical for building public confidence and ensuring that AI innovations serve societal good. R&D teams should conduct impact assessments at the design phase to anticipate potential risks and incorporate mitigation strategies from the outset. This forward-looking approach minimizes surprises and strengthens the ethical foundation of AI projects.
Continuous monitoring and evaluation are also crucial after deployment. AI systems are dynamic and can evolve in unexpected ways, so ongoing oversight is necessary to ensure they remain compliant with the RMF and continue to operate as intended. This iterative feedback loop helps refine both the AI system and the risk management processes themselves.
Ultimately, integrating the AI RMF into the R&D lifecycle transforms how AI is built, moving towards a future where innovation is synonymous with responsibility and trust.
Practical Steps for R&D Teams by Mid-2025
With the mid-2025 deadline approaching, R&D teams must take concrete, actionable steps to ensure compliance with the NIST AI RMF. This involves more than just reading the framework; it requires active implementation and a shift in mindset. Procrastination is not an option, as the effort required to embed these changes can be substantial, particularly for complex AI systems.
The first practical step is to conduct an internal audit of all current and planned AI projects. Identify which projects fall under the scope of the RMF and assess their current level of compliance. This audit should highlight areas of strength and, more importantly, areas where significant work is needed. Prioritize projects based on their risk profile and potential impact.
The next crucial step is to establish a dedicated AI RMF compliance team or designate specific individuals responsible for overseeing implementation. This team should comprise members from various disciplines, including AI engineers, data scientists, legal experts, ethicists, and project managers. Their collective expertise will be invaluable in navigating the multidisciplinary challenges posed by the framework.
Actionable Compliance Checklist
- Develop an AI Governance Policy: Formalize roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes for AI risk management.
- Implement Risk Assessment Tools: Utilize or develop tools to systematically identify, analyze, and evaluate AI risks.
- Establish Data Provenance and Quality Standards: Ensure data used for AI development is reliable, unbiased, and ethically sourced.
- Create Explainability and Transparency Protocols: Document how AI models make decisions and communicate these explanations clearly.
- Conduct Regular AI System Audits: Periodically review AI systems for performance, bias, and compliance.
Furthermore, invest in training and education for all R&D personnel. Ensuring that every team member understands the principles of the NIST AI RMF and their role in upholding them is paramount. This includes awareness training for developers, specific training for risk managers, and ethical considerations for all involved in AI projects. By mid-2025, a robust understanding and practical application of the RMF should be deeply ingrained in the R&D culture.
In summary, preparing for NIST AI RMF compliance by mid-2025 demands a strategic, multi-faceted approach involving audits, dedicated teams, clear policies, and comprehensive training. These steps will not only ensure adherence but also cultivate a culture of responsible AI innovation.
Addressing Ethical AI Concerns in R&D
Ethical AI concerns are at the heart of the NIST AI RMF, presenting R&D teams with a critical challenge and an opportunity to lead responsibly. Beyond technical performance, the ethical implications of AI systems, such as bias, fairness, privacy, and accountability, profoundly impact society. Addressing these concerns effectively requires a proactive and integrated approach throughout the R&D process.
One of the primary ethical challenges is algorithmic bias. AI models trained on biased data can perpetuate and even amplify societal inequalities, leading to unfair outcomes. R&D teams must implement rigorous data auditing processes to identify and mitigate biases in training datasets. This includes not only statistical analysis but also qualitative reviews to understand the social context of the data.
Strategies for Mitigating Ethical Risks
- Bias Detection and Mitigation: Employ tools and methodologies to identify and reduce bias in datasets and AI models.
- Human-in-the-Loop Design: Integrate human oversight and intervention points in AI systems, especially for critical decisions.
- Privacy-Preserving AI: Utilize techniques like differential privacy and federated learning to protect sensitive information.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involve diverse stakeholders, including ethicists and affected communities, in the AI development process.
Transparency and explainability are also crucial for ethical AI. Users and regulators need to understand how AI systems arrive at their decisions, especially in high-stakes applications. R&D teams should focus on developing interpretable models and creating clear documentation that explains the model’s logic, limitations, and potential impacts. This fosters trust and enables accountability.
Furthermore, establishing internal ethical review boards or committees can provide an additional layer of scrutiny for AI projects. These boards can assess potential ethical risks, provide guidance, and ensure that projects align with organizational values and societal expectations. Their independent perspective can help identify blind spots and promote a more holistic approach to ethical AI development.
In conclusion, addressing ethical AI concerns in R&D is not just about compliance but about building AI that is fair, transparent, and beneficial for all. By integrating ethical considerations from the outset, R&D teams can develop AI systems that uphold societal values and earn public trust.
Resource Allocation and Training for Compliance
Effective compliance with the NIST AI RMF by mid-2025 hinges significantly on appropriate resource allocation and comprehensive training. Organizations must recognize that achieving compliance is not just a technical task but a strategic investment requiring dedicated personnel, financial resources, and time. Underestimating these needs can lead to rushed implementations, superficial adherence, and ultimately, non-compliance.
Resource allocation begins with identifying the human capital required. This includes training existing R&D staff, potentially hiring new experts in AI ethics, governance, or risk management, or designating specific roles for RMF oversight. Cross-functional teams are essential, bringing together legal, technical, and ethical perspectives to ensure a holistic approach to risk management. Financial resources must be set aside for these personnel, as well as for new tools, software, and external consulting if needed. These investments are critical for building a robust compliance infrastructure.
Essential Training Modules
- RMF Fundamentals: Overview of the NIST AI RMF, its purpose, and core functions for all R&D staff.
- Ethical AI Principles: Deep dive into fairness, transparency, accountability, and privacy in AI development.
- Risk Assessment Techniques: Practical training on identifying, measuring, and mitigating AI-specific risks.
- Data Governance and Bias Detection: Best practices for managing data quality, provenance, and addressing algorithmic bias.
Beyond human resources, organizations must consider technological resources. This might involve investing in AI governance platforms, specialized software for bias detection, or tools for explainable AI (XAI). These technologies can automate certain aspects of compliance, streamline risk assessment processes, and provide valuable insights into AI system behavior. Choosing the right tools requires careful evaluation to ensure they integrate seamlessly with existing R&D workflows.
Moreover, ongoing training and continuous learning are vital. The field of AI is rapidly evolving, and so too will the risks and best practices for managing them. Regular workshops, seminars, and access to up-to-date resources will ensure that R&D teams remain knowledgeable and adaptable. Fostering a culture of learning and open discussion about AI risks and ethics is paramount for long-term compliance and responsible innovation.
In conclusion, successful NIST AI RMF compliance by mid-2025 demands strategic resource allocation—both human and technological—coupled with continuous, comprehensive training. This investment ensures that R&D teams are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of AI risk management effectively.
Future-Proofing Your AI R&D Strategy
Future-proofing your AI R&D strategy involves not only meeting the current NIST AI RMF requirements but also anticipating future regulatory changes and technological advancements. The AI landscape is dynamic, and a static approach to compliance will quickly become obsolete. Organizations must build adaptable and resilient strategies that can evolve with the industry, ensuring long-term trustworthiness and innovation.
One key aspect of future-proofing is to adopt a principles-based approach rather than merely focusing on checklist compliance. While the RMF provides a valuable framework, understanding the underlying principles of responsible AI—such as fairness, transparency, and accountability—allows R&D teams to apply these concepts to new technologies and unforeseen challenges. This deep understanding enables proactive adaptation rather than reactive scrambling.
Building an Adaptive AI Governance Model
- Modular Frameworks: Design AI systems and governance processes that are modular and can be easily updated or extended.
- Scenario Planning: Conduct regular horizon scanning and scenario planning to anticipate emerging AI risks and ethical dilemmas.
- Cross-Industry Collaboration: Engage with industry consortia, academic institutions, and regulatory bodies to stay abreast of best practices.
- Continuous Feedback Loops: Establish mechanisms for ongoing feedback from users, stakeholders, and internal teams to refine AI systems and risk management processes.
Investing in explainable AI (XAI) and robust AI testing methodologies is another critical component of future-proofing. As AI systems become more complex, the ability to understand their internal workings and verify their performance will be paramount. R&D teams should prioritize research into advanced XAI techniques and develop comprehensive testing protocols that go beyond traditional software testing to include fairness, robustness, and adversarial attack resistance.
Furthermore, fostering a culture of ethical innovation within R&D is essential. This means encouraging open dialogue about the societal implications of AI, empowering researchers to raise concerns, and rewarding responsible development practices. A strong ethical culture ensures that future AI innovations are not only technically brilliant but also socially beneficial and trustworthy.
In conclusion, future-proofing your AI R&D strategy requires a forward-thinking mindset, a principles-based approach to governance, continuous investment in XAI and testing, and a robust ethical culture. By embracing these elements, organizations can ensure their AI innovations remain relevant, compliant, and impactful for years to come.
Benefits of Proactive AI RMF Compliance
Embracing proactive compliance with the NIST AI RMF offers a multitude of benefits that extend far beyond simply avoiding penalties. For R&D organizations, it transforms potential liabilities into strategic advantages, fostering innovation, enhancing reputation, and building long-term trust with stakeholders. This forward-thinking approach positions companies as leaders in responsible AI development.
One of the most significant benefits is enhanced innovation. By systematically identifying and mitigating risks early in the R&D process, teams can explore new AI applications with greater confidence. A clear understanding of ethical boundaries and compliance requirements allows for more focused and responsible experimentation, reducing the likelihood of costly missteps later on. It encourages the development of AI systems that are inherently more robust and reliable.
Furthermore, proactive compliance significantly strengthens an organization’s reputation. In an era where public scrutiny of AI is increasing, demonstrating a commitment to ethical and responsible AI development can be a powerful differentiator. It builds trust with customers, partners, and regulators, positioning the organization as a trustworthy leader in the AI space. This positive reputation can attract top talent and open doors to new collaborations.
Strategic Advantages of Early Adoption
- Reduced Legal and Reputational Risk: Minimize exposure to lawsuits, fines, and public backlash by addressing risks pre-emptively.
- Improved AI System Quality: Develop more reliable, fair, and transparent AI systems through integrated risk management.
- Competitive Advantage: Differentiate from competitors by showcasing a commitment to responsible AI innovation.
- Enhanced Public Trust: Build stronger relationships with users and stakeholders through transparent and ethical practices.
Another crucial benefit is operational efficiency. Integrating RMF principles into the R&D lifecycle streamlines processes and reduces the need for reactive interventions. By embedding risk assessments and ethical considerations from the start, organizations can avoid expensive redesigns, retesting, and legal challenges that often arise from neglecting these aspects during initial development. This leads to faster time-to-market for trustworthy AI solutions.
Finally, proactive compliance fosters a culture of responsibility and excellence within R&D. It encourages team members to think critically about the broader impact of their work, promoting a more thoughtful and ethical approach to AI development. This internal culture strengthens the organization’s overall commitment to responsible innovation, ensuring sustained success in the evolving AI landscape.
In conclusion, proactively adopting the NIST AI RMF offers substantial benefits, from accelerating responsible innovation and bolstering reputation to improving operational efficiency and fostering a culture of ethical excellence. It’s a strategic imperative for any R&D organization aiming for long-term success in AI.
| Key Aspect | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| RMF Core Functions | Govern, Map, Measure, Manage AI risks throughout the lifecycle. |
| R&D Integration | Embed risk management and ethical considerations from design to deployment. |
| Ethical AI Focus | Address bias, fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI systems. |
| Compliance Deadline | Mid-2025 for implementing practical steps and establishing governance. |
Frequently Asked Questions About AI RMF Compliance
The primary goal of the NIST AI RMF is to provide organizations with a flexible and voluntary framework to better manage the risks associated with artificial intelligence. It aims to foster the development and deployment of trustworthy AI systems by promoting practices that address potential harms, biases, and ethical concerns throughout the AI lifecycle.
Mid-2025 marks a crucial period as organizations are expected to have made significant progress in integrating the NIST AI RMF into their operations. This deadline encourages R&D teams to proactively establish governance, implement risk assessment processes, and train personnel to ensure their AI innovations align with federal guidelines and best practices for responsible AI.
The RMF emphasizes addressing algorithmic bias by encouraging rigorous data auditing, implementing bias detection and mitigation techniques, and promoting fairness in AI design. It stresses the importance of diverse datasets and continuous monitoring to ensure AI systems do not perpetuate or amplify existing societal inequalities, leading to more equitable outcomes.
Essential resources for R&D compliance include dedicated human capital (trained staff, AI ethicists), financial investment for new tools and training, and technological resources like AI governance platforms. Comprehensive training programs on RMF fundamentals, ethical AI, and risk assessment techniques are also critical to ensure all team members are well-equipped.
Long-term benefits of proactive RMF compliance include enhanced innovation, reduced legal and reputational risks, improved AI system quality, and a significant competitive advantage. It fosters greater public trust and positions the organization as a leader in responsible AI development, ensuring sustained success and positive societal impact in the evolving AI landscape.
Conclusion
Navigating the new NIST AI Risk Management Framework by mid-2025 is a crucial undertaking for any R&D organization involved in artificial intelligence. This framework is not merely a set of regulations but a comprehensive guide to developing and deploying AI systems responsibly and ethically. By proactively integrating its principles into every stage of the AI lifecycle, from initial design to ongoing monitoring, R&D teams can mitigate risks, foster innovation, and build trustworthy AI. The investment in resource allocation, comprehensive training, and a strong ethical culture will undoubtedly yield significant returns, enhancing reputation, reducing liabilities, and ultimately contributing to a more beneficial and equitable AI future. Embracing the NIST AI RMF is a strategic imperative for long-term success and leadership in the rapidly evolving world of artificial intelligence.





